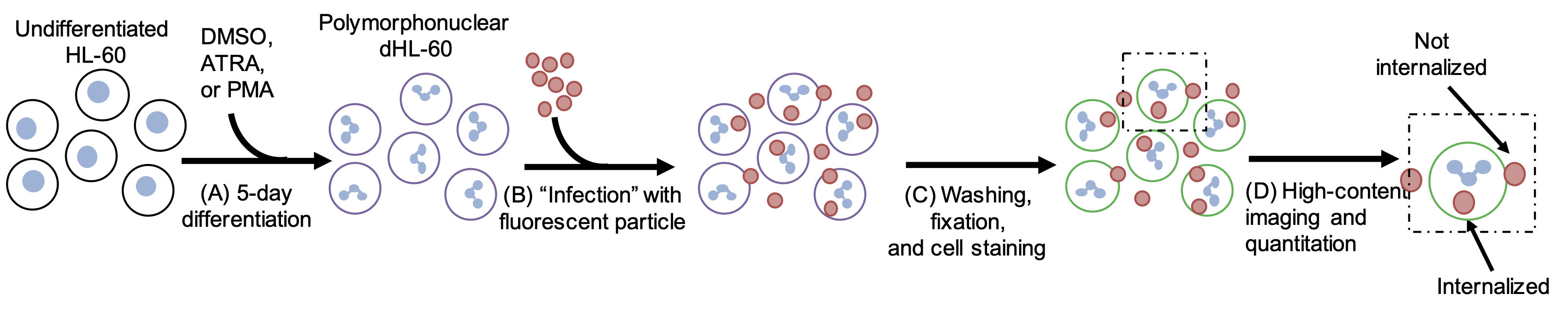
Dissertation Chapter 4: Sealing the Gaps
Sphingolipids are essential for repairing the endosomal damage caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
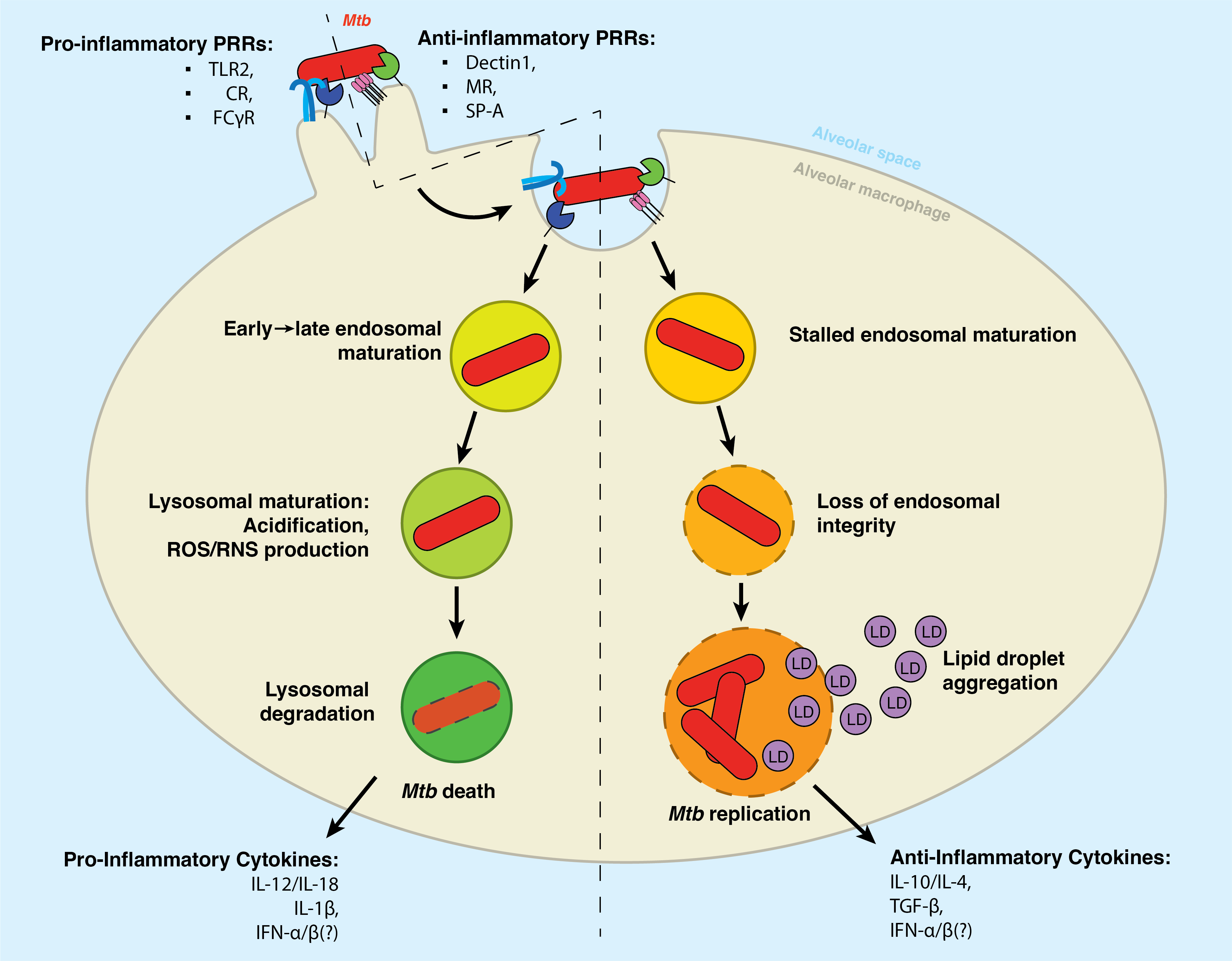
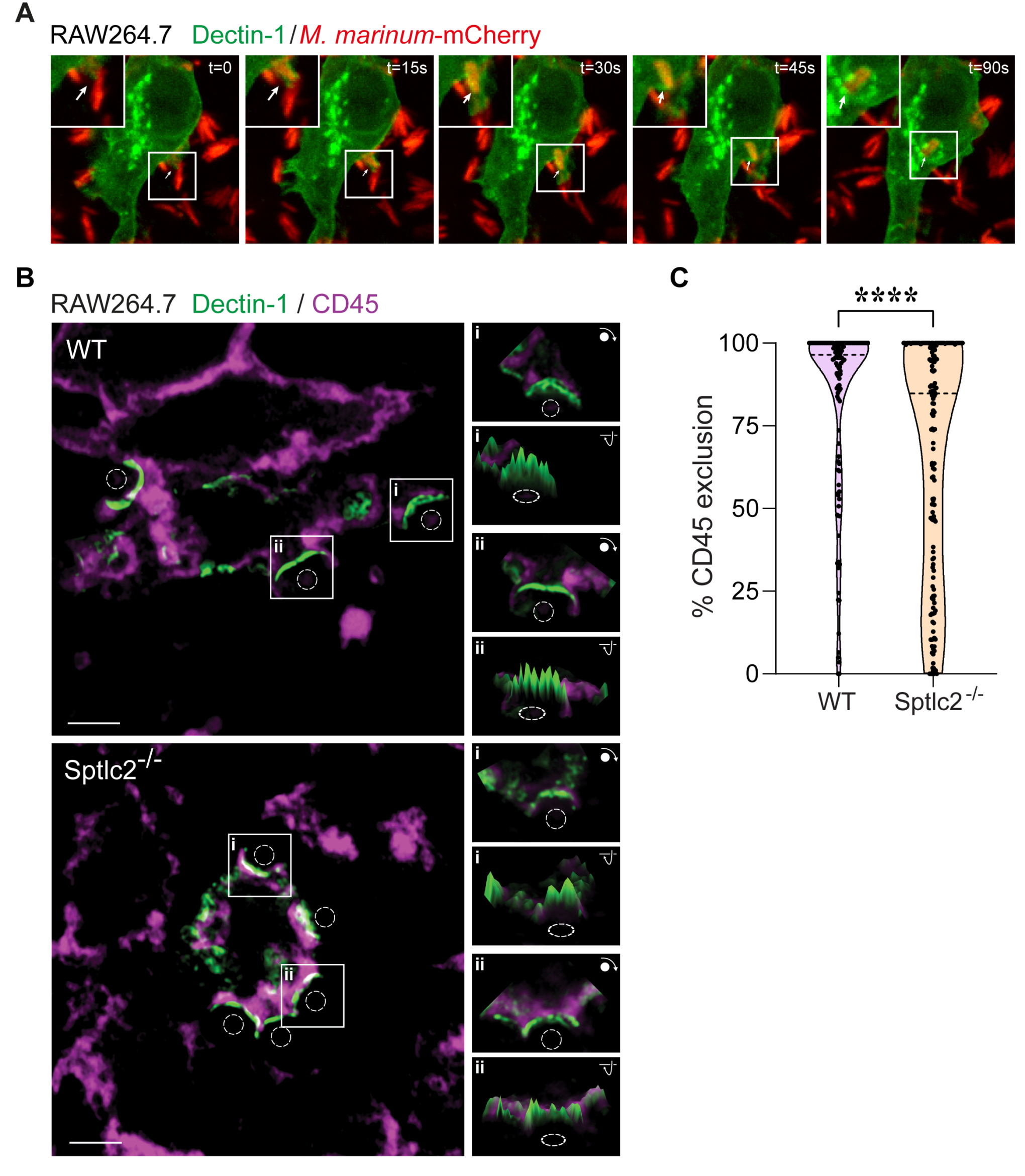
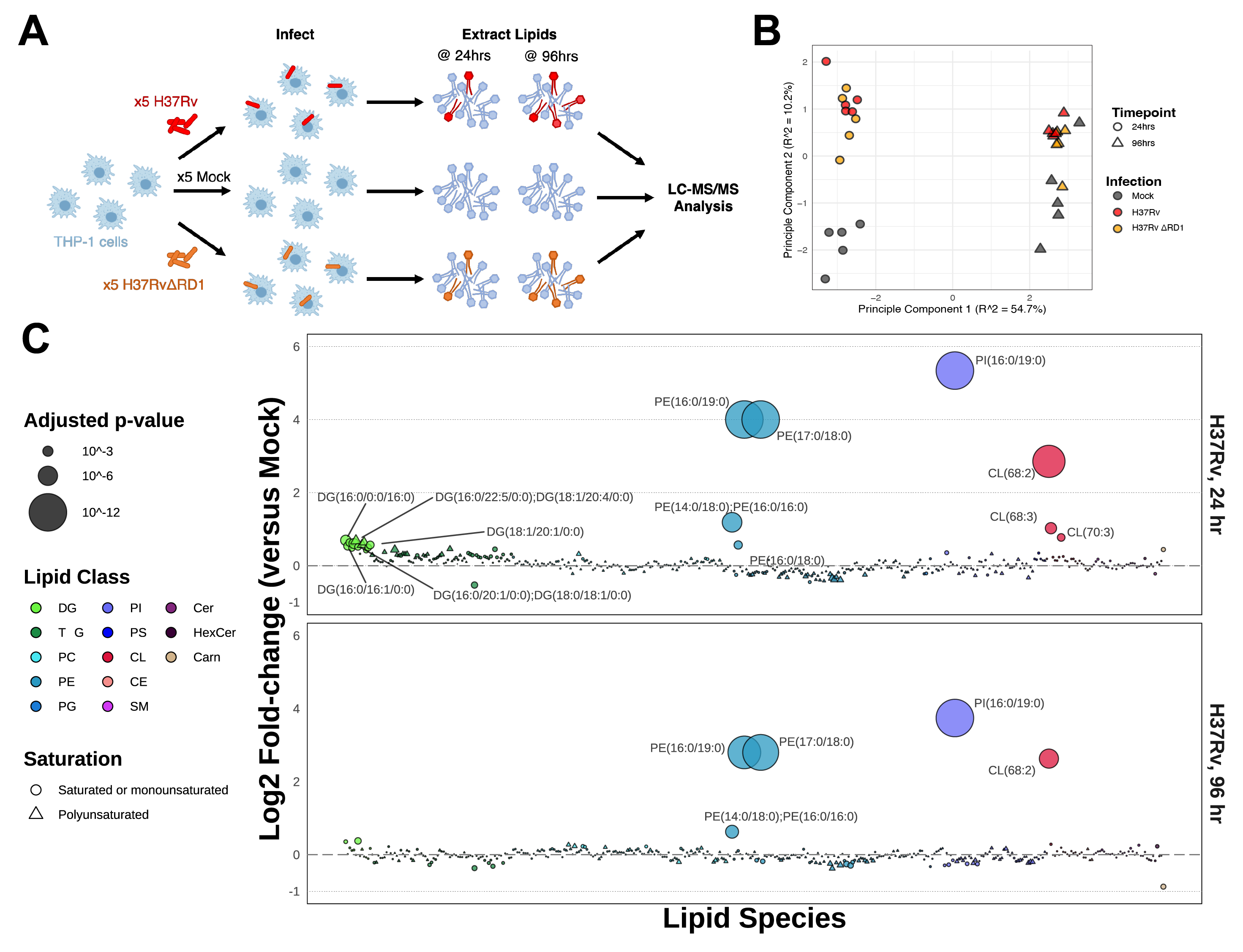
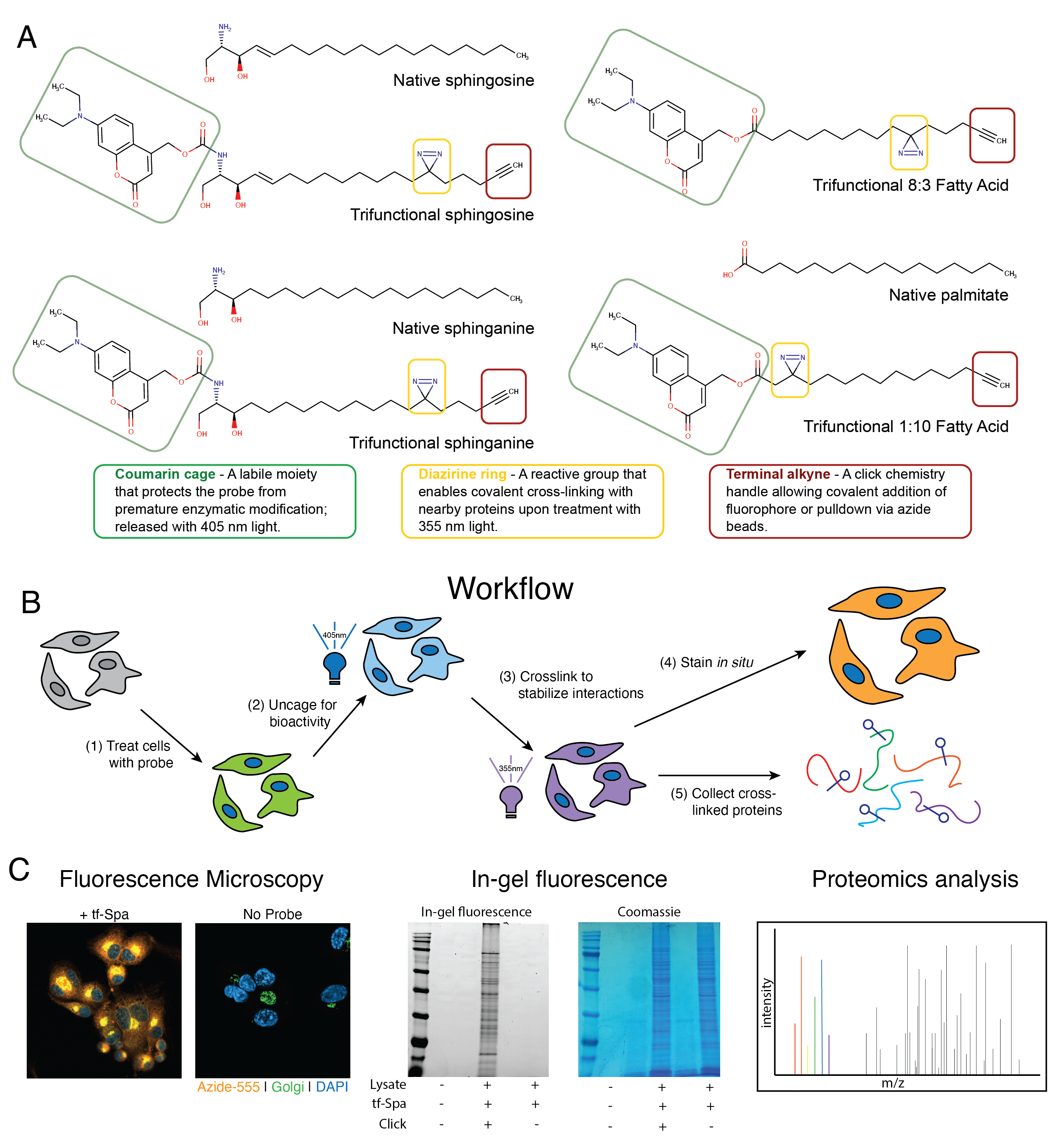
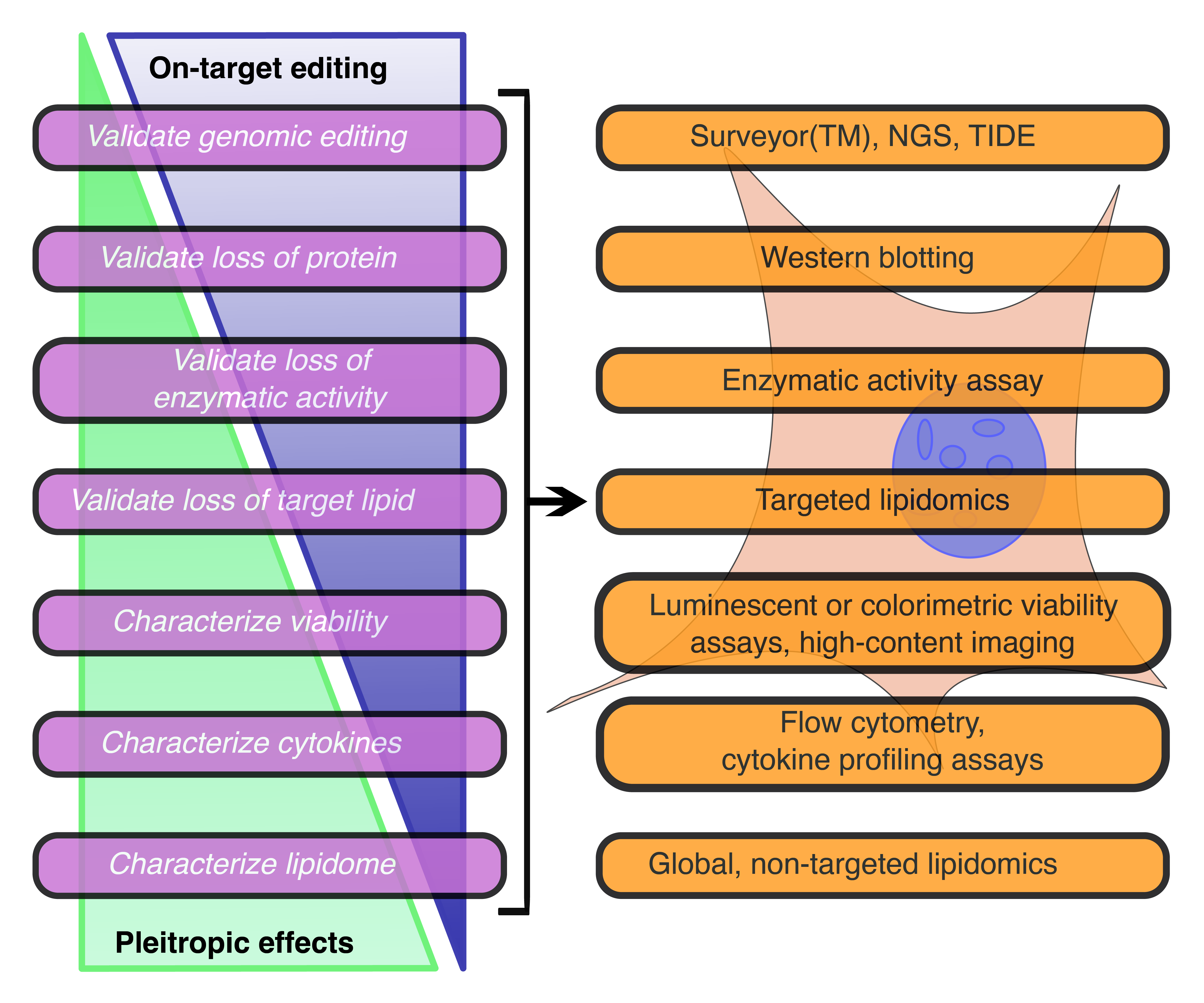
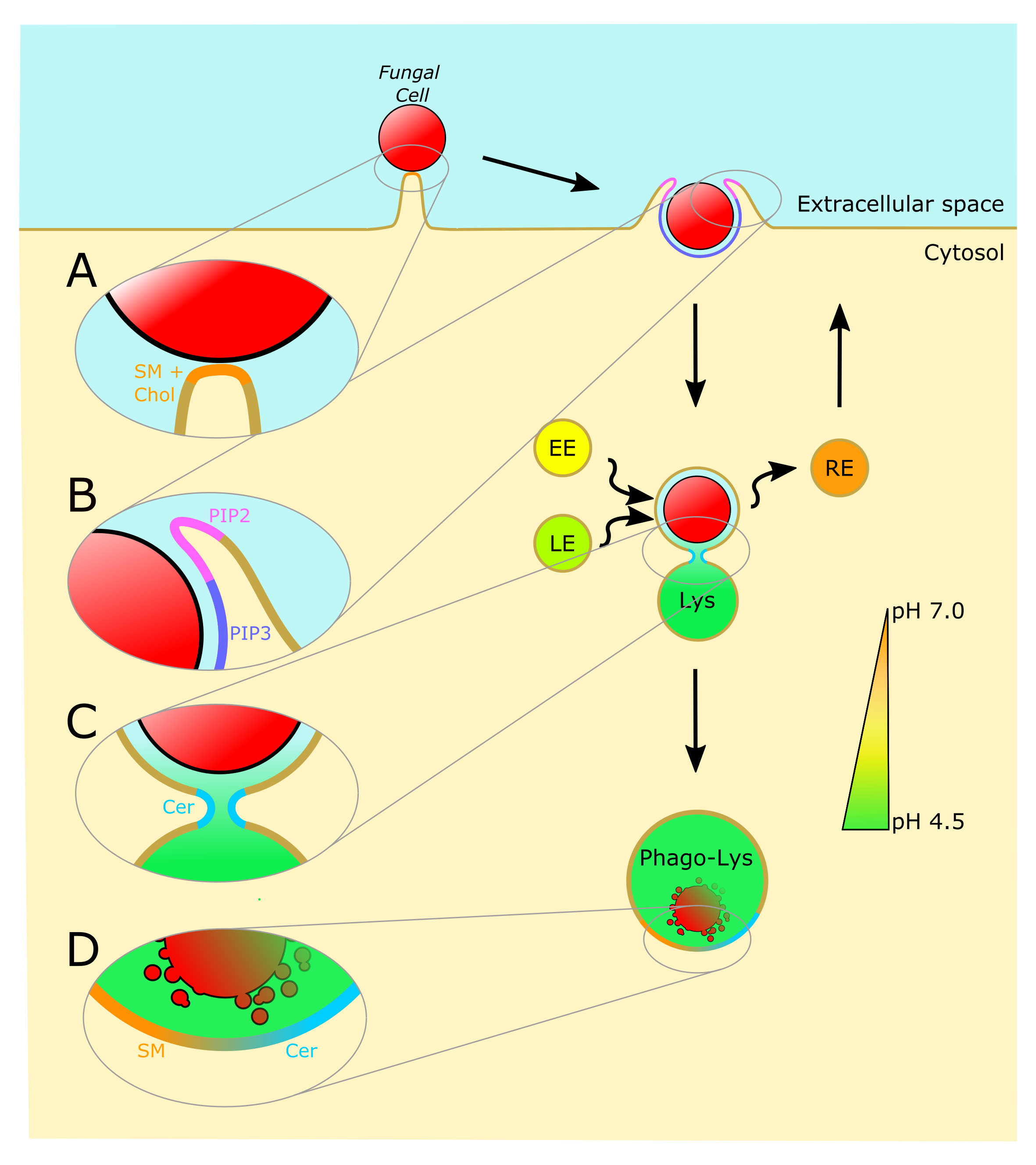
Tuberculosis infection remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, causing over 1.3 million deaths in 2022 alone. With the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), there is a pressing need for novel and improved therapeutics. Here, we characterize the critical role of sphingolipids in restricting intracellular replication of Mtb. Sphingolipids are essential for rapidly responding to membrane damage and maintaining lysosomal integrity during Mtb infection. Additionally, sphingolipids enable the restriction of Mtb growth within host cells. Understanding the influence of host sphingolipids on Mtb infection may reveal novel routes for host-directed therapy. This research provides valuable insights into the pathogenesis of Mtb infection and could pave the way for developing new therapeutic strategies.
Abstract
Tuberculosis infection remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, causing over 1.3 million deaths in 2022 alone. With the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), there is a pressing need for novel and improved therapeutics. Here, we characterize the critical role of sphingolipids in restricting intracellular replication of Mtb. Sphingolipids are essential for rapidly responding to membrane damage and maintaining lysosomal integrity during Mtb infection. Additionally, sphingolipids enable the restriction of Mtb growth within host cells. Understanding the influence of host sphingolipids on Mtb infection may reveal novel routes for host-directed therapy. This research provides valuable insights into the pathogenesis of Mtb infection and could pave the way for developing new therapeutic strategies.
Click here if you are not redirected!
No matching items